

A type of software testing, non functional testing is a major testing term that encapsulates various productive testing techniques to evaluate and assess the non-functional traits of a software application. Prime purpose of this testing methodology is to evaluate the competency and effectiveness of an application, under variant and unforeseen conditions. This type of software testing can be seen as one stop solution for various software related questions, such as:
Non-functional testing can be categorized into various types of testing, which are mentioned below:
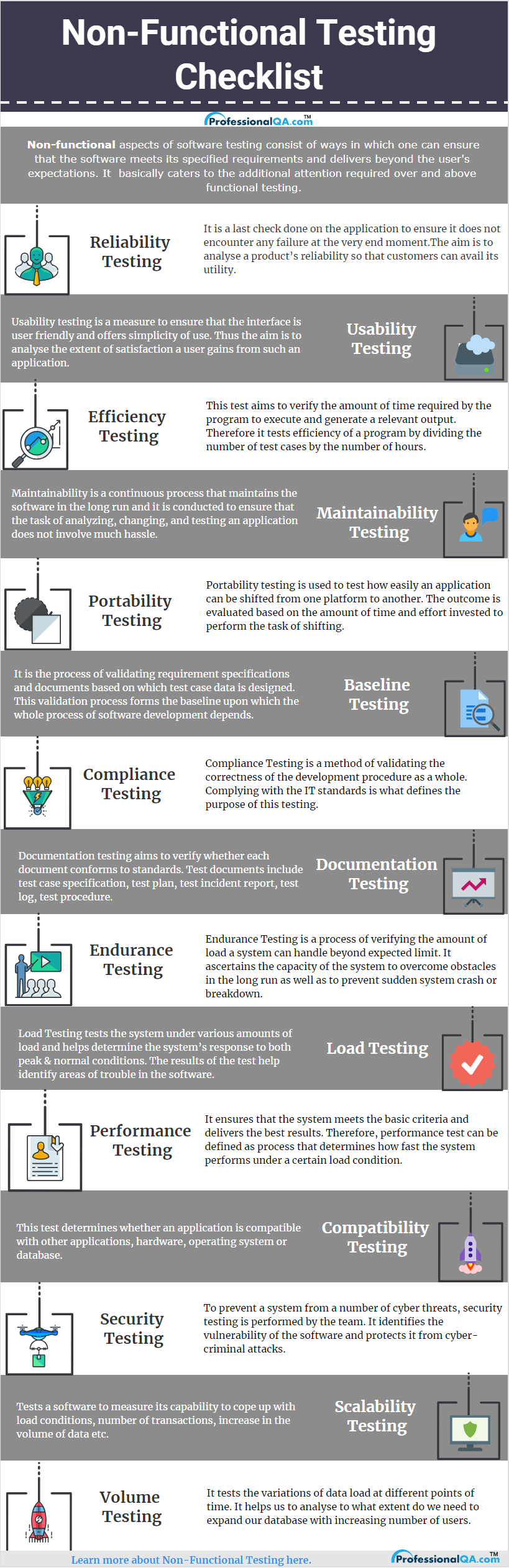
Availability Testing is an approach of testing the integrated system testing, contrary to what is available for its operational requirements. It is carried out to ensure the 24*7 availability of software application to perform its intended functionalities, whenever required without getting failed.
This testing is necessary to evaluate the compatibility of a software product with its expected working environment including multiple platforms, OS, devices, software and hardware to execute its intended functionalities properly without any issues.
Configuration testing is performed to ensure that the final product works seamlessly with the supported & different software and hardware configuration.
Also known by the name of conformance testing, compliance testing is used to ensure the software functioning and performance in accordance to company's established standards & guidelines.
Also known as "implementation testing", this testing technique is used to evaluate and assess the expected functioning of the software, post its successful installation and simultaneously ensuring no issues or errors during the process of software installation, upgrades and un-installation.
To examine the documentation artifacts, prepared before and during the Software development and testing phase such as various requirements, specifications, plans, strategies and other related and tangible elements, documentation testing of the system is carried out as a part of non-functional testing
One of the simplest types of performance testing which is used to system's performance in terms of its behaviour & response under variant load factors.
Testing software capability or durability to endure huge and constant load, consistently for a longer period time falls under the technique of endurance testing.
The purpose of localization testing is to verify the quality of the software's local attributes targeted for a particular population/culture/region to ensure the correct and expected functioning of the localized version for a particular region to meet the needs & expectations of the targeted audience whereas internationalization testing concerns with the overall uniform functionality of the software globally, across all different geographical regions.
A major testing methodology involving different testing techniques to examine the response, stability, scalability, reliability and other quality metrics of a software product under real world environment and conditions.
Maintainability testing is used to evaluate the capability of the software application to get easily upgraded or modified in order to meet the growing needs & requirements of the users.
This testing involves the wilful failure or crash of the software application in order to assess its ability to get recovered and fully functional, quickly.
Security testing is used to verify and validate the security features of the software, including identification and detection of security loopholes and other related vulnerabilities so as to ensure the protection, authenticity, confidentiality and integrity of information and data stored in or shared with the system.
Covering load and feature testing under its belt, software reliability gives a measure of the product’s life cycle between two failures and the time it takes to repair. For further reading, please visit Reliability testing
In volume testing, software product is subjected to or burdened with huge amount of data so as to measure and assess the response, behaviour and effectiveness of the application.volume testing
Scalability testing ensures that the system should be scalable, in proportion to increase in the load, number of concurrent users, data size, etc. whenever required.
This testing technique is being used to evaluate the user-friendliness features of the system to ensure no issues to the end-users while using and handling the system.
An extreme form of load testing under performance testing methodology which emphasizes on robustness feature of software product by making it functioning under severe and extreme conditions apart from the gradually increasing load on the system.
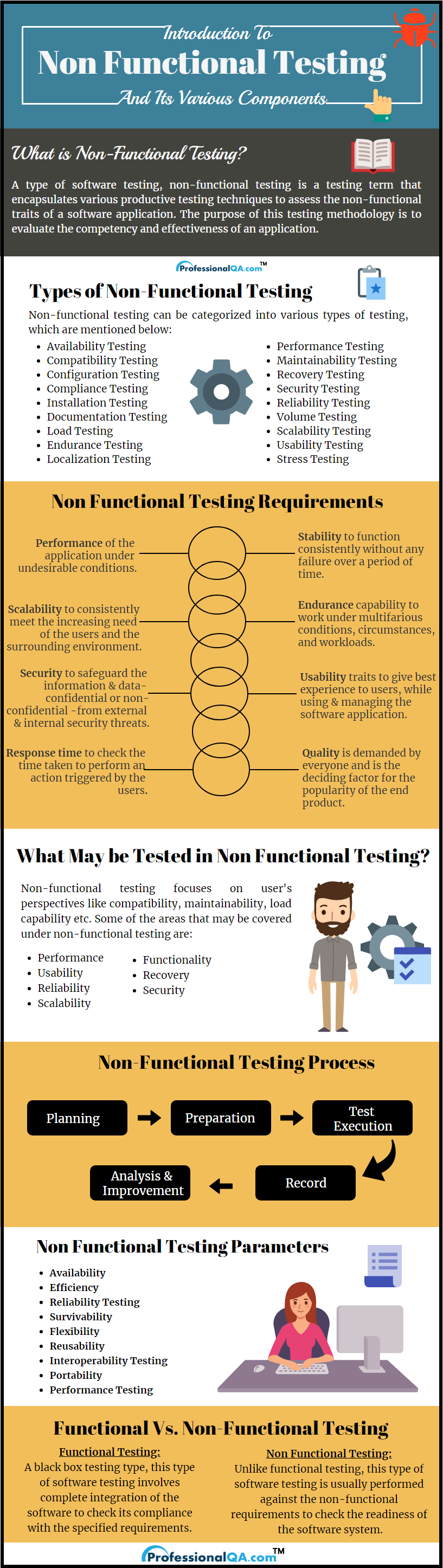
Nonfunctional requirements are immensely important as they specify how the system behaves in terms of constraints and prerequisites. Non-functional requirements have a great impact on the whole software development & testing process as well as its cost and resource planning. Hence, these should always be taken into consideration during the project’s cost estimation phase. Some of these requirements are:
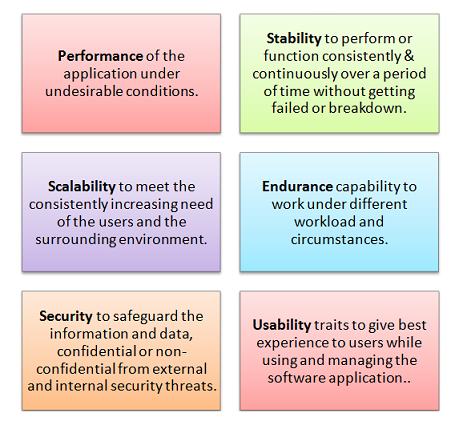
Besides these requirements, there are few other requirements of non-functional testing. Read our new article to know more about functional & non-functional requirements.
Unlike functional testing which is based on pre-defined requirements and specifications, non-functional testing focuses on user's perspectives like compatibility, maintainability, load capability etc. Some of the areas that may be covered under non-functional testing are
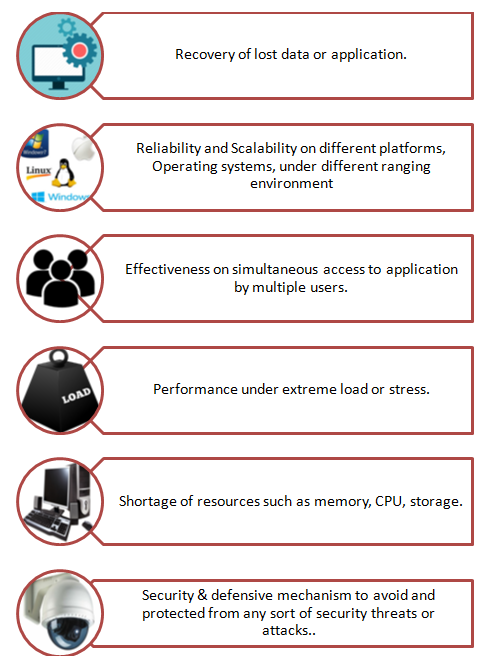
The process of non-functional testing involves six important stages, wherein the team of testers plan and work together to test the functional requirements and the readiness of a system. Therefore, the process of non functional testing is:
There are various parameters for non-functional testing, each of which are extremely vital for getting accurate as well as expected results. These ensure that the application meets the requirements of the client and offers them exceptional quality, performance, features, etc. Therefore, some of these parameters are:
The list of non functional parameters is quite non-exhaustive, therefore here is a non functional testing checklist for you to help you with the whole process.
A discussion of non-functional testing is incomplete without a proper comparison between functional and non-functional testing. Functional testing and non-functional testing are both integral part of Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC) and play a major role in developing a bug free software with unique features, performance, scalability, and more.
A black box testing type, this type of software testing involves complete integration of the software to check its compliance with the specified requirements. Performed both manually and with the assistance of tools, functional testing is a crucial quality assurance process. This is usually executed with the assistance of smoke testing, sanity testing, regression testing, and usability testing.
Unlike functional testing, this type of software testing is usually performed against the non-functional requirements to check the readiness of the software system. The main focus of non-functional testing is to ensure optimum customer & user experience.
For a detailed comparison of functional Testing and non functional testing, click here.
Non Functional Testing is as important as the functional testing is. Without verifying and validating the interoperability across multiple platforms, maintainability, security, portability and other miscellaneous features, we cannot guarantee the product readiness for its market release and extensive use by the users in the real environment and factors.
Advertisement: